Rocketwaveuk
Man`s Space Journey
The Apolllo Story And Video
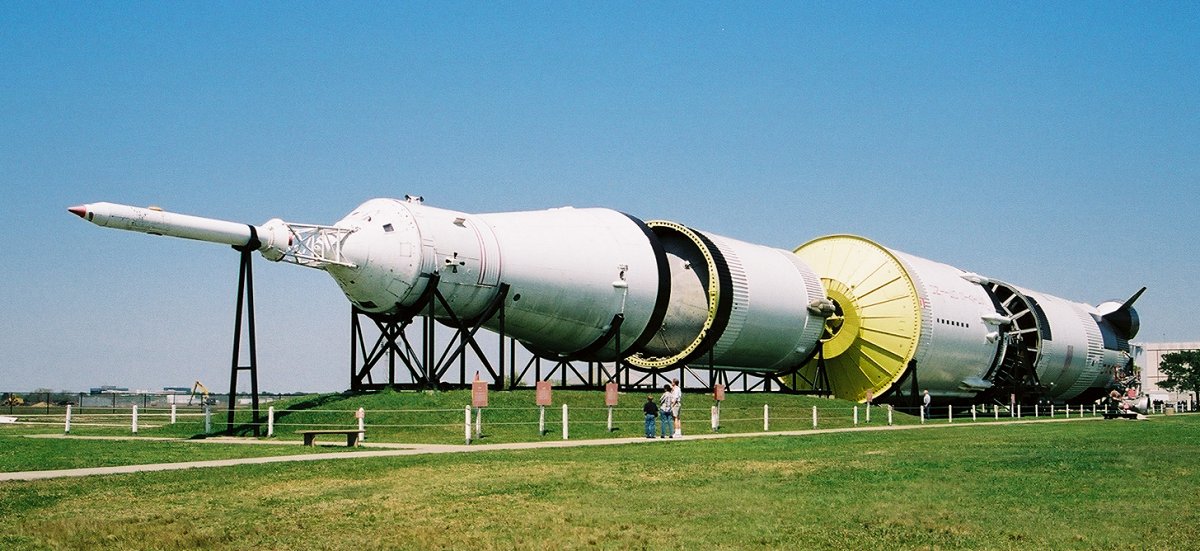
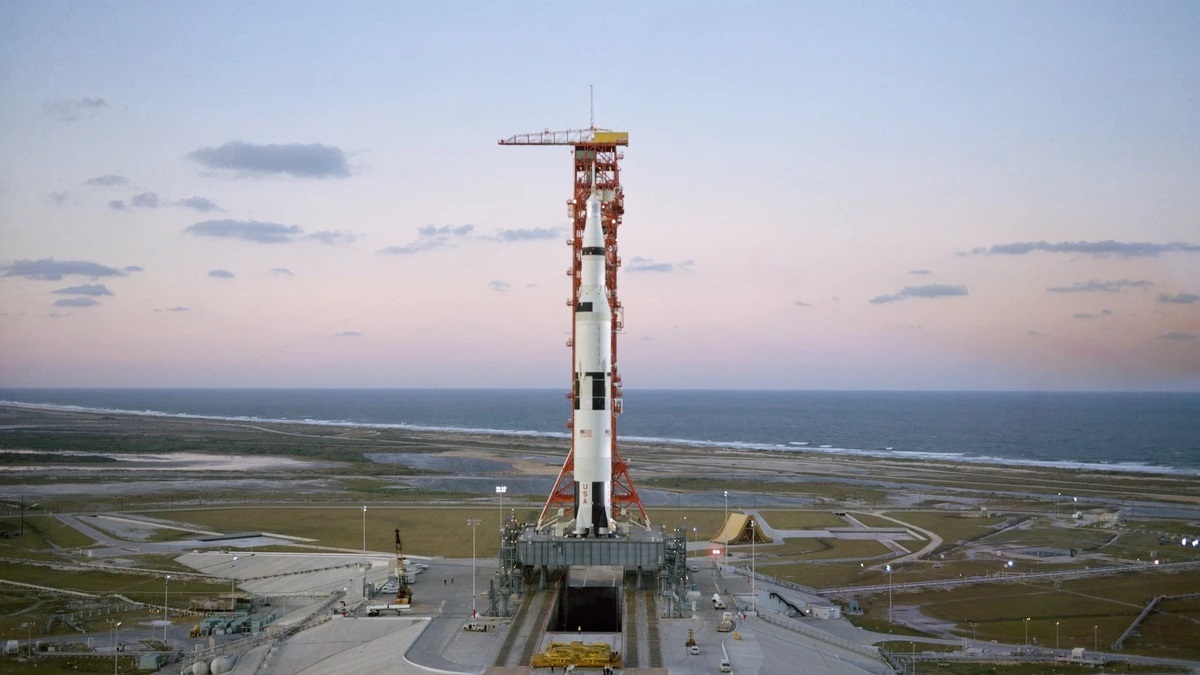
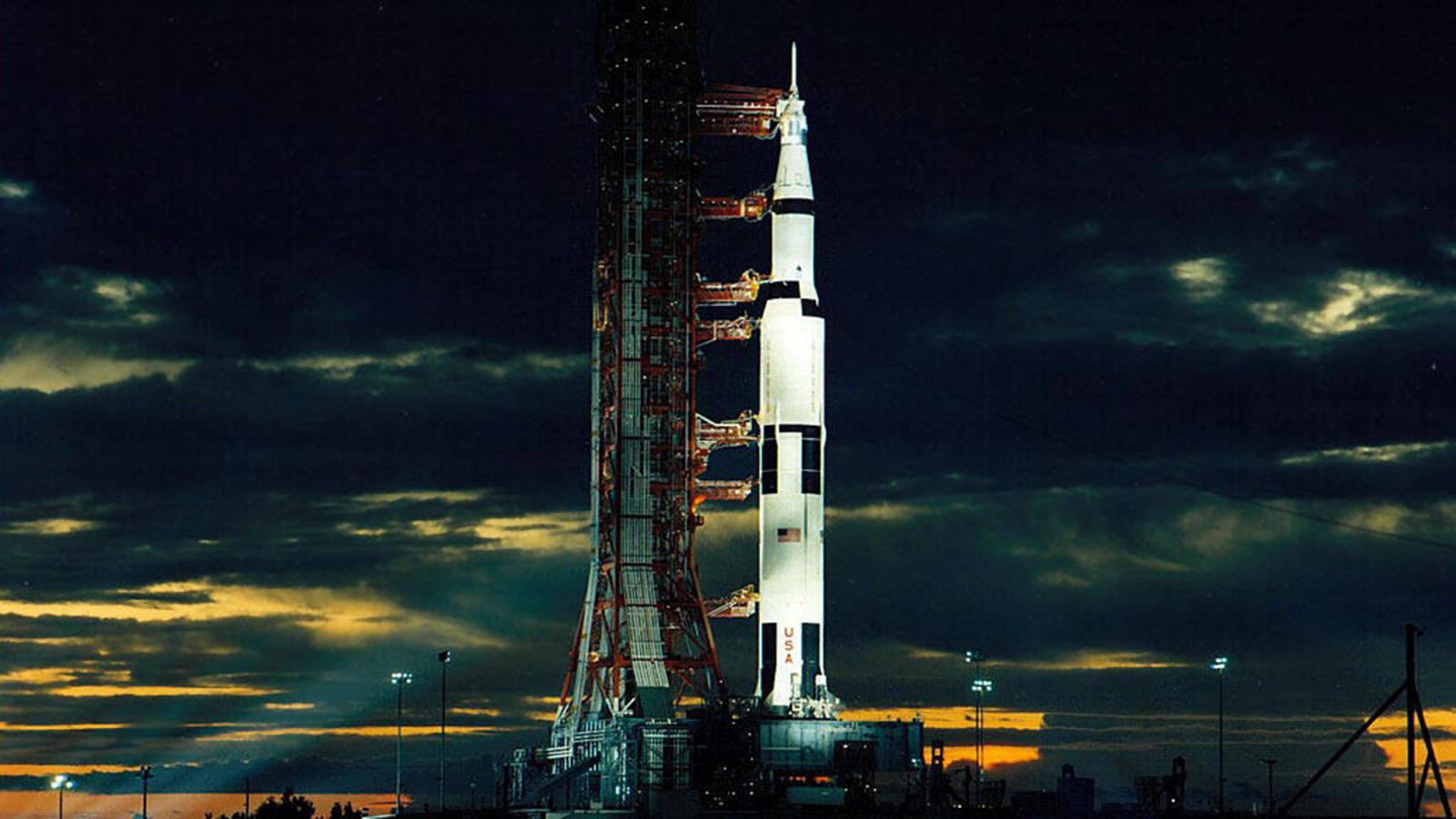
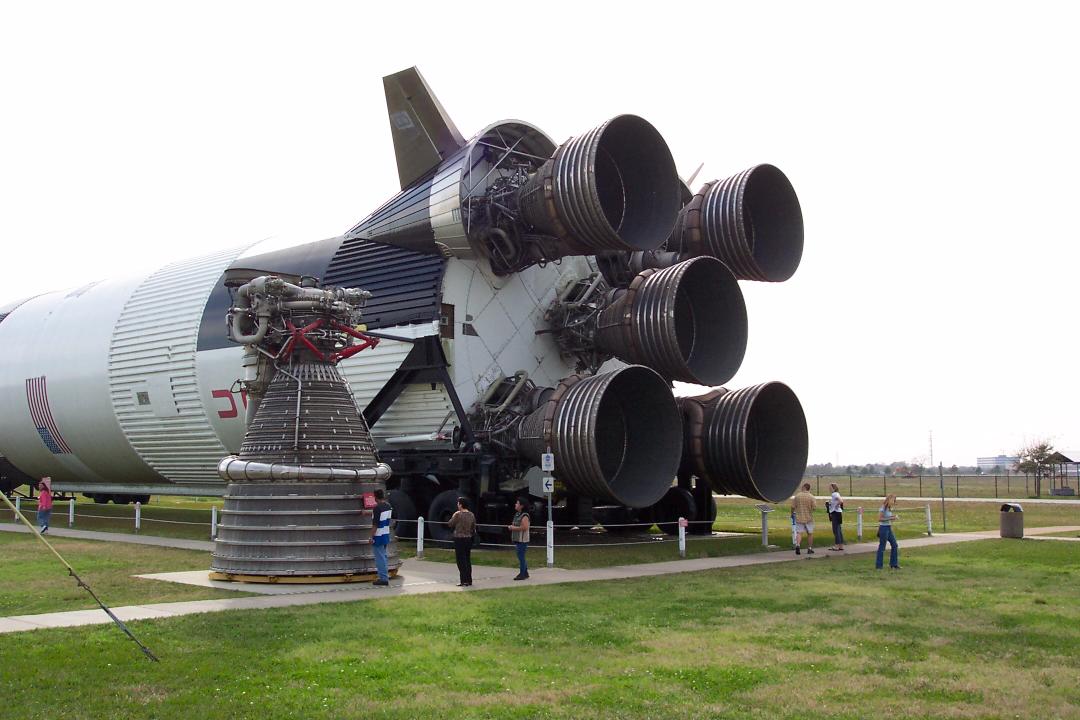
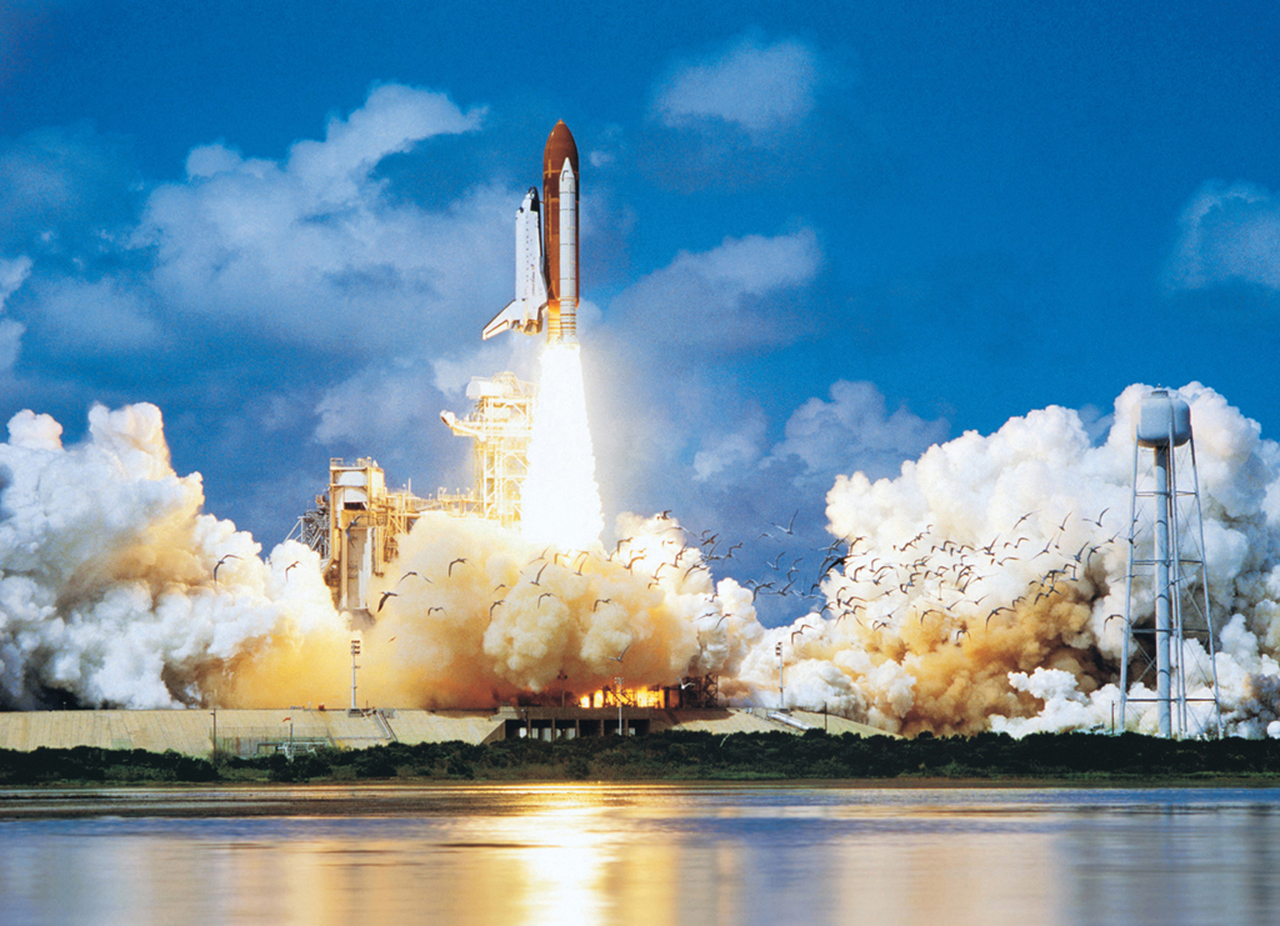
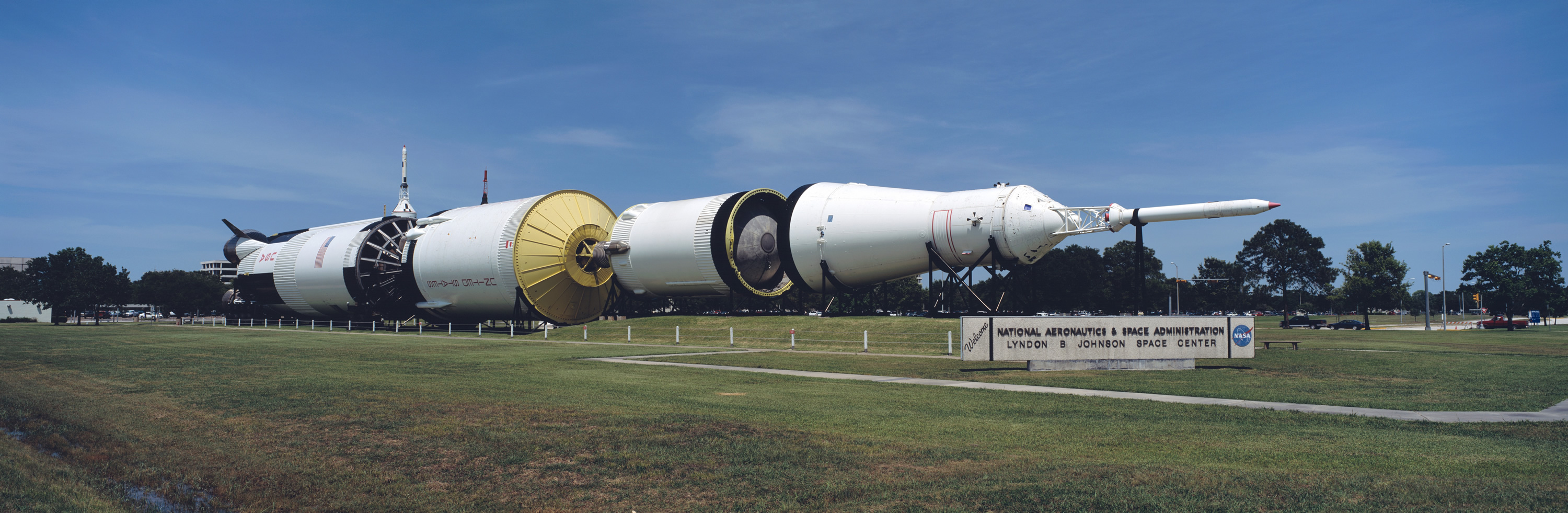
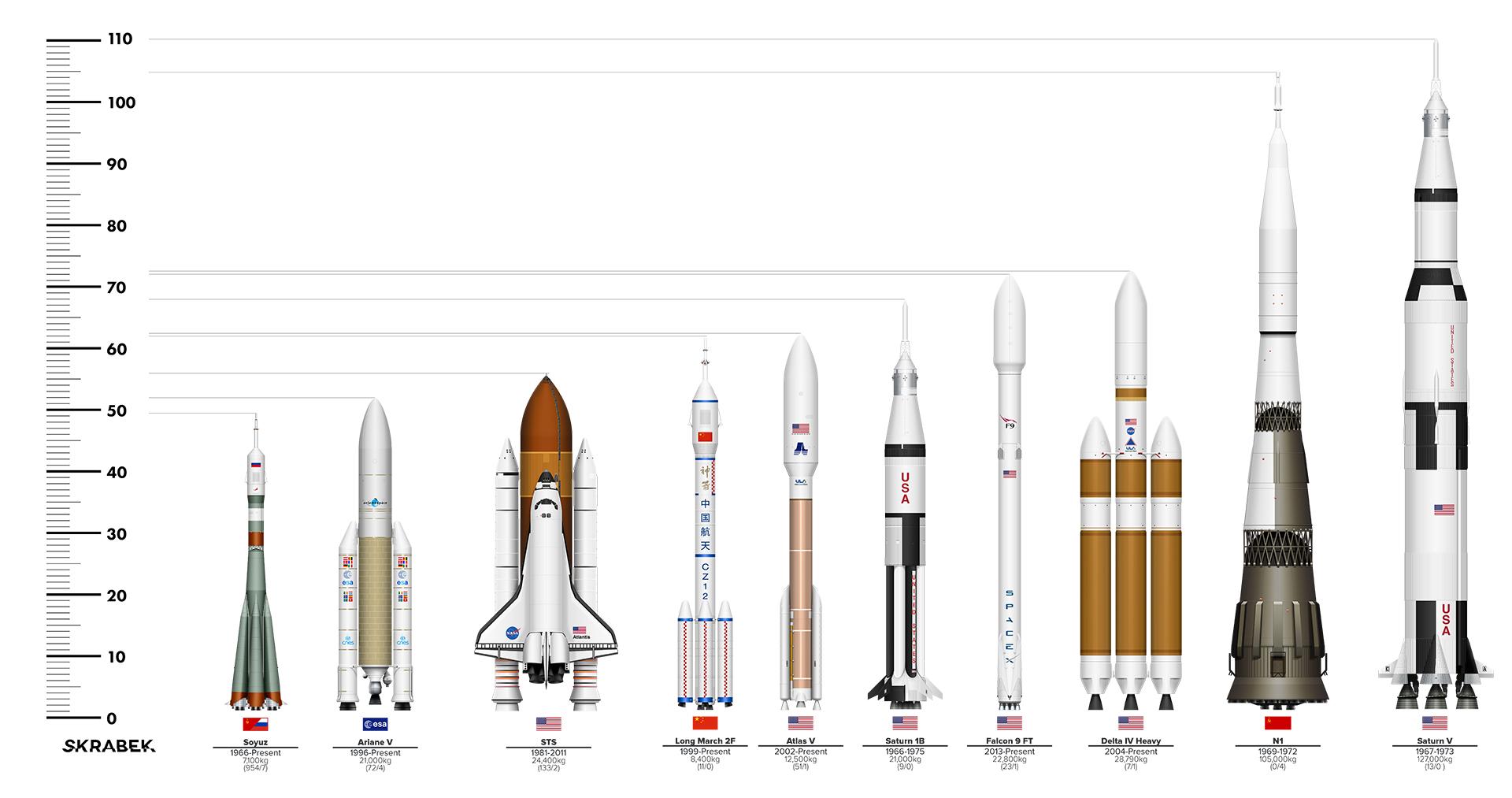
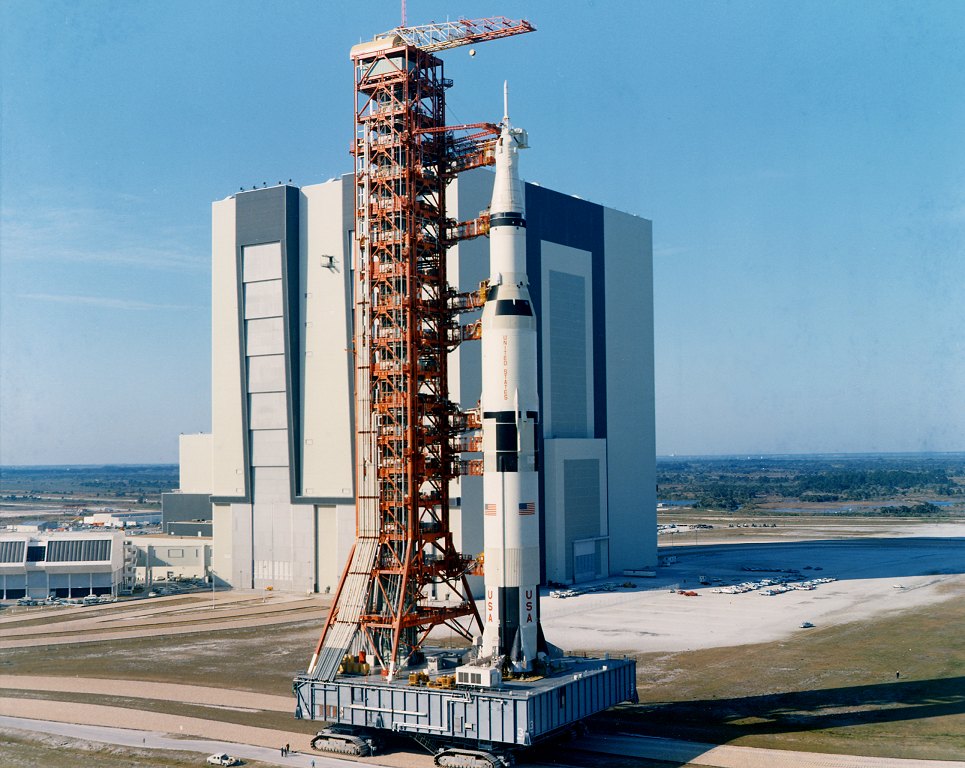
The Saturn V was a rocket NASA built to send people to the moon. (The V in the name is the Roman numeral five.)
The Saturn V was a type of rocket called a Heavy Lift Vehicle.
It was the most powerful rocket that had ever flown successfully.
The Saturn V was used in the Apollo program in the 1960s and 1970s. I
t also was used to launch the Skylab space station.The Saturn V rocket was 111 meters (363 feet) tall,
about the height of a 36-story-tall building.
Fully fueled for liftoff, the Saturn V weighed 2.8 million kilograms (6.2 million pounds), the weight of about 400 elephants.
The rocket generated 34.5 million newtons (7.6 million pounds) of thrust at launch,
creating more power than 85 Hoover Dams. It could launch about 118,000 kilograms (130 tons) into Earth orbit.
That's about as much weight as 10 school buses. The Saturn V could launch about 43,500 kilograms (50 tons) to the moon.
The Saturn V was developed at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Centre . It was one of three types of Saturn rockets NASA built.
Two smaller rockets, the Saturn I (1) and IB (1b), were used to launch humans into Earth orbit.
The Saturn V sent them beyond Earth orbit to the moon. The first Saturn V was launched in 1967. I
t was called Apollo 4. Apollo 6 followed in 1968. Both of these rockets were launched without crews.
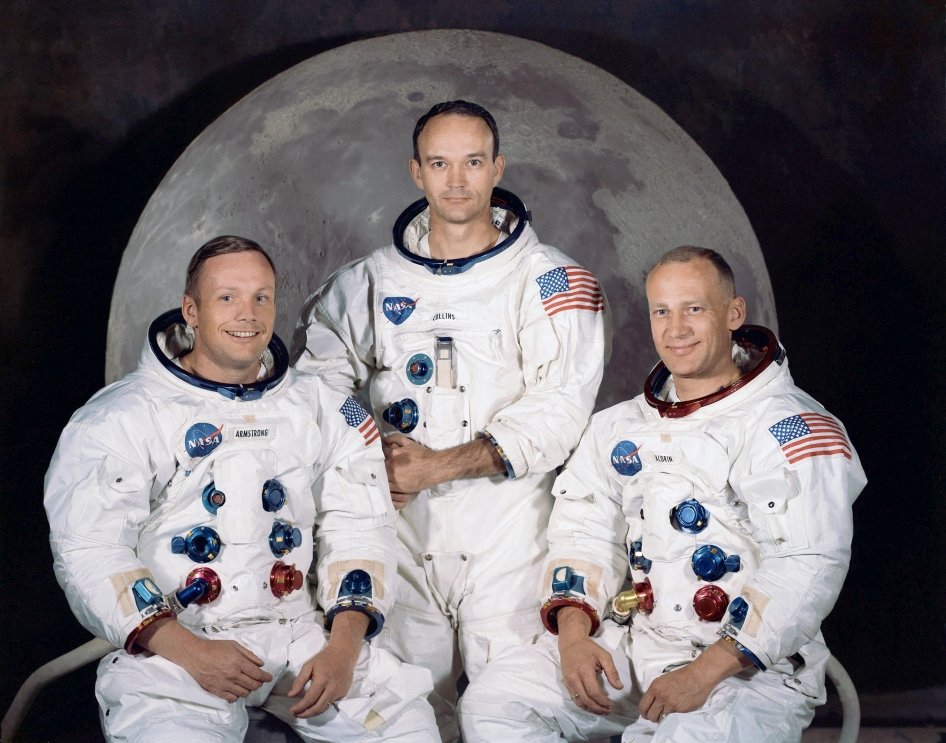
These launches tested the Saturn V rocket. The first Saturn V launched with a crew was Apollo 8. On this mission,
astronauts orbited the moon but did not land. On Apollo 9, the crew tested the Apollo moon Lander
by flying it in Earth orbit without landing. On Apollo 10, the Saturn V launched the lunar Lander to the moon.
The crew tested the Lander in space but did not land it on the moon. In 1969,
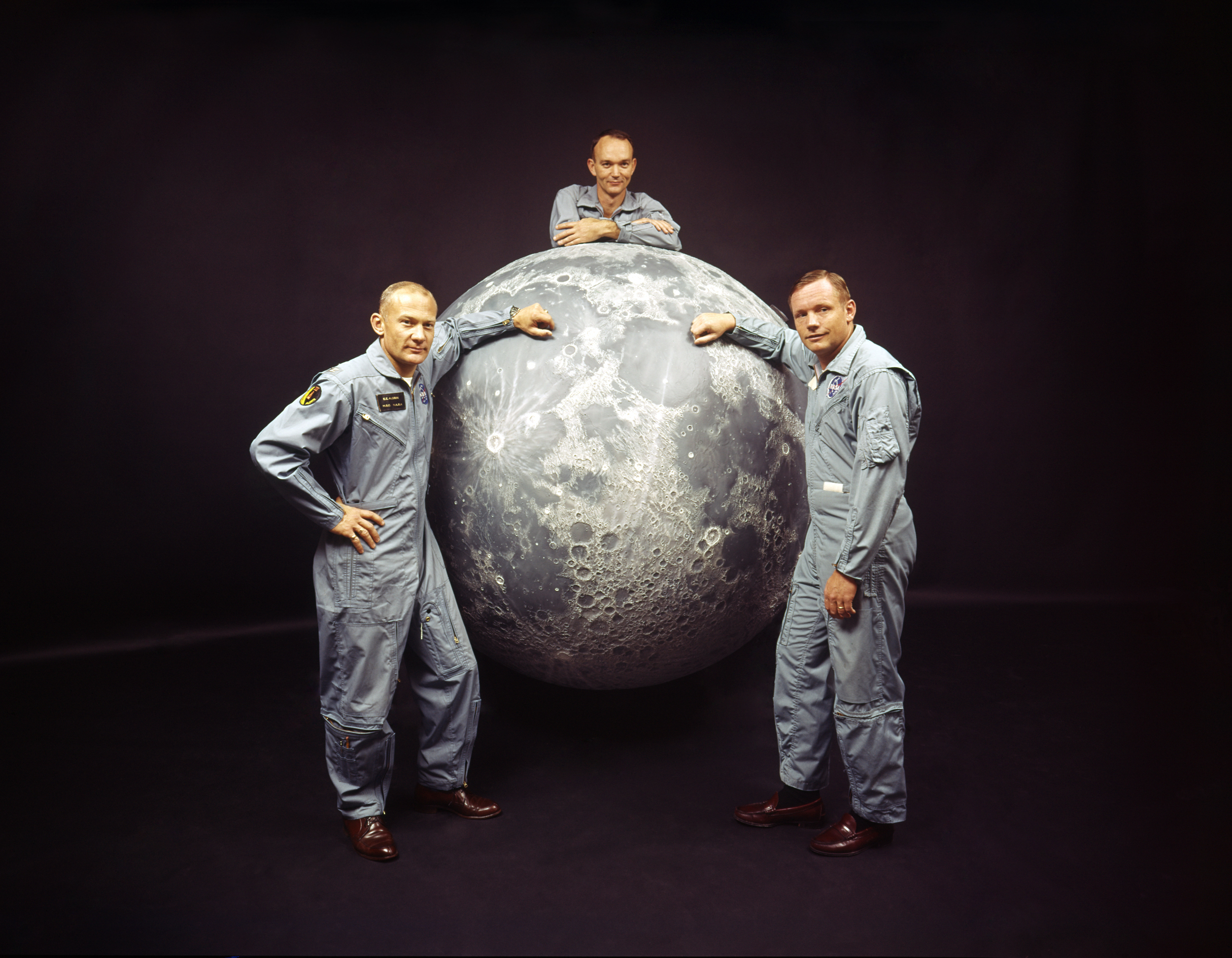
Apollo 11 was the first mission to land astronauts on the moon. Saturn V rockets also made it possible for
astronauts to land on the moon on Apollo 12, 14, 15, 16 and 17. On Apollo 13, the Saturn V lifted the crew into space.
But after a Capsule failure and a heroic effort by NASA and the crew the capsule did a slingshot around the moon before the
dramatic but safe return of the crew .
The last Saturn V was launched in 1973, without a crew. It was used to launch the Skylab space station into Earth orbit.
At 363 feet/111 meters long, it is 60 feet/18 meters taller than the Statue of Liberty.
A total of 13 Saturn V rockets were launched between 1967 and 1972.
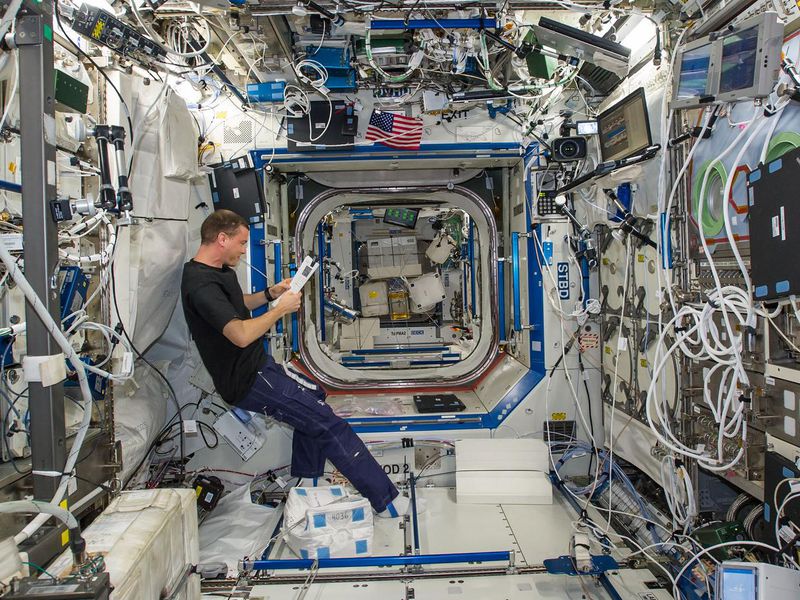
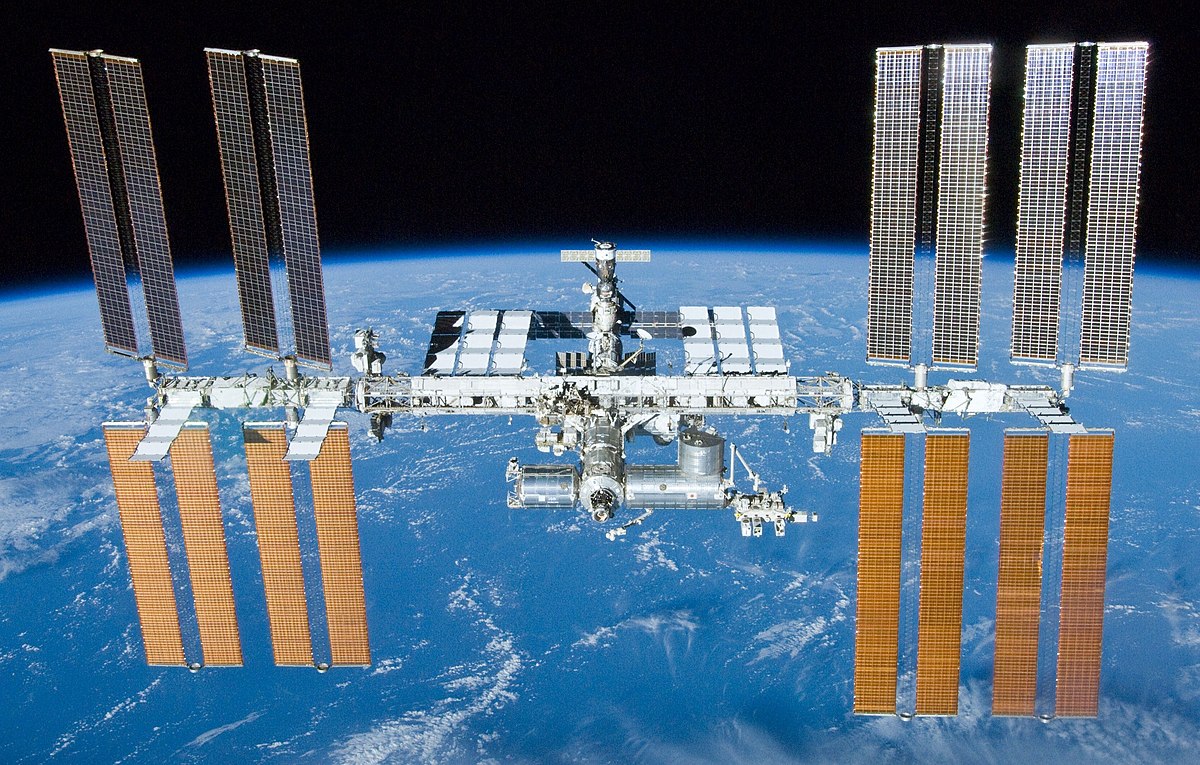
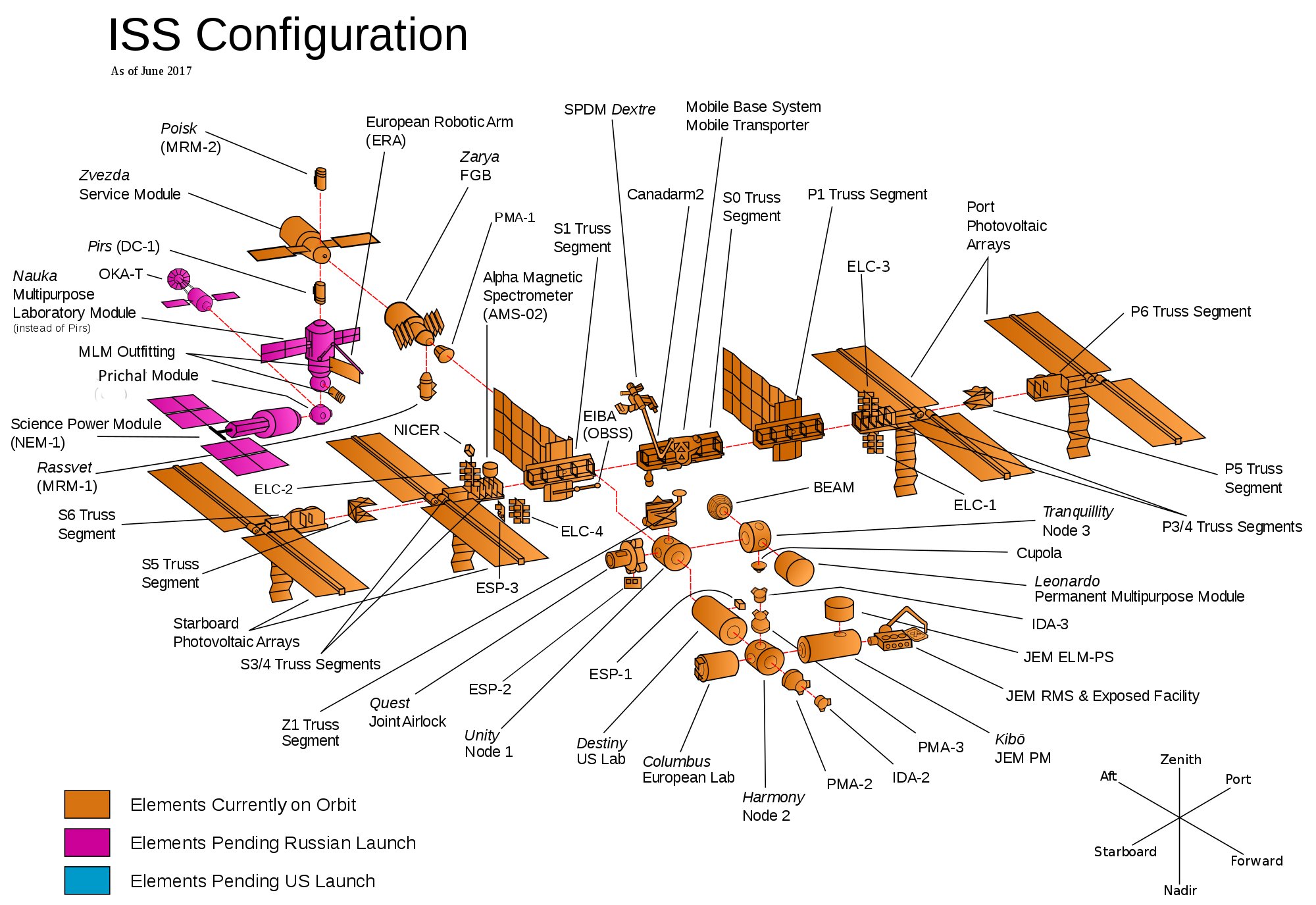
The Internation Space Station
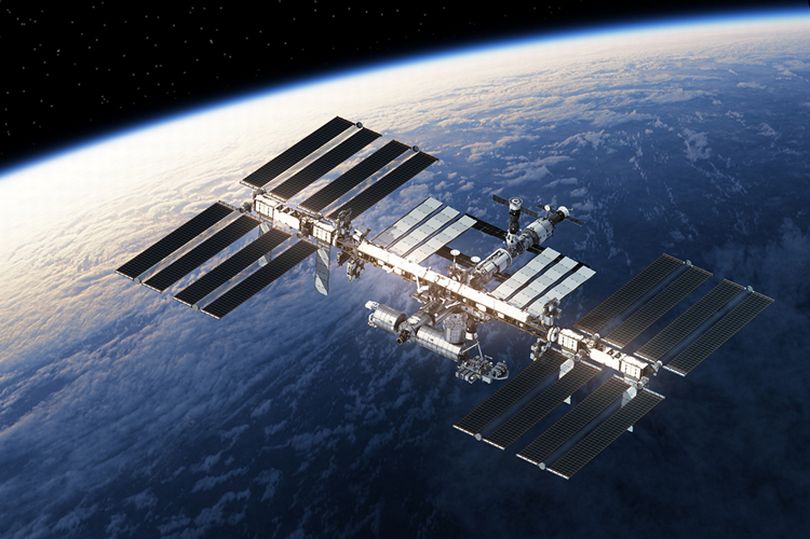

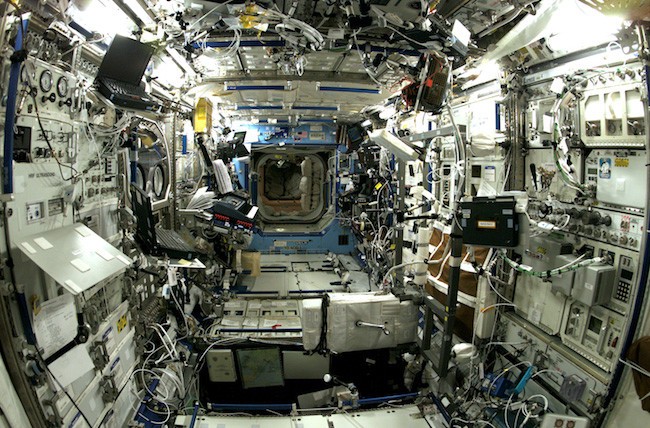
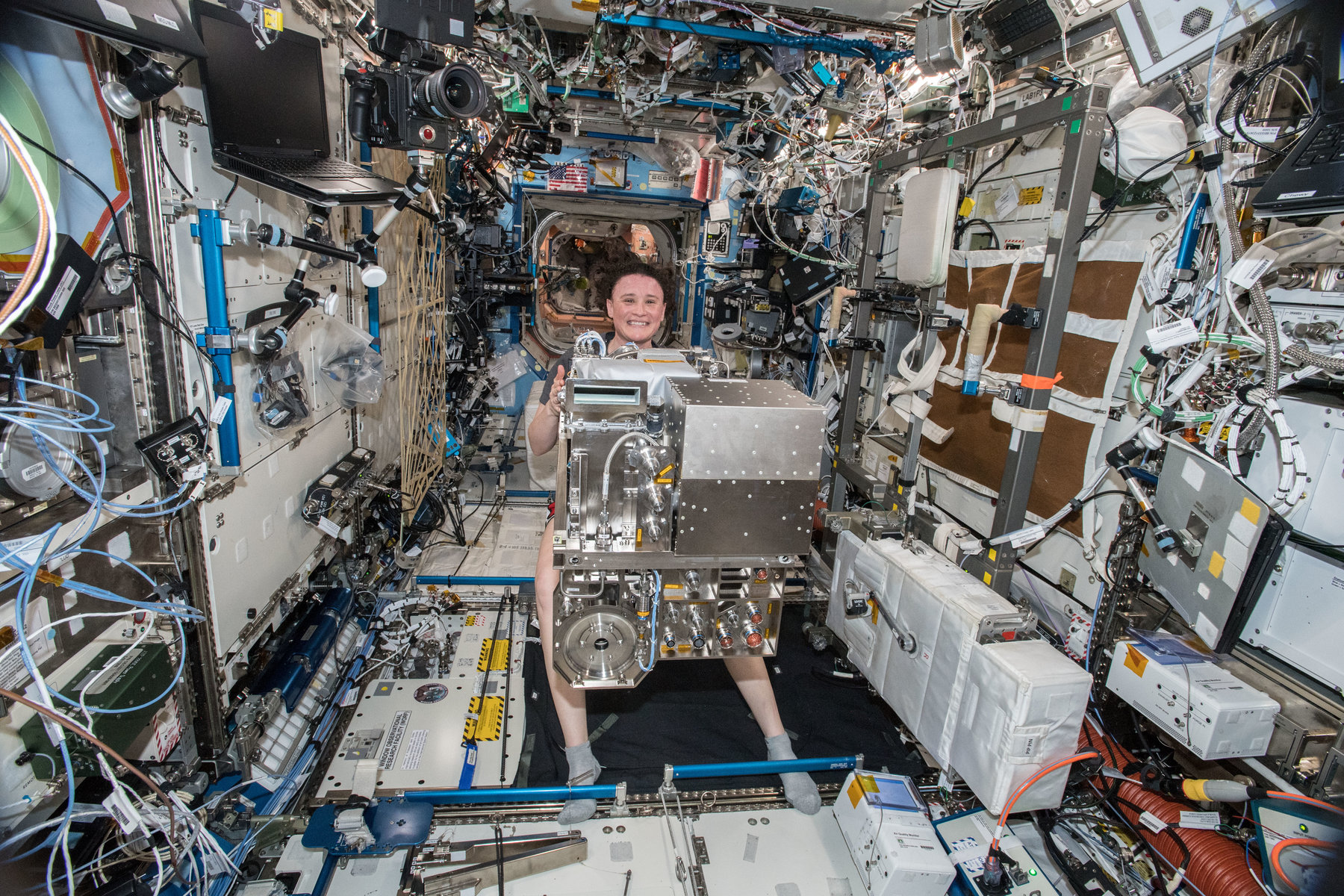
The International Space Station (ISS) is a modular space station ( artificial satellite) in low Earth orbit.
The ISS programme is a multi-national collaborative project between five participating space agencies:
NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), JAXA (Japan), ESA (Europe), and CSA (Canada).
The ownership and use of the space station is established by intergovernmental treaties and agreements.
It evolved from the Space Station Freedom proposal.
The Hubble Telescope
The Soyuz Rockets
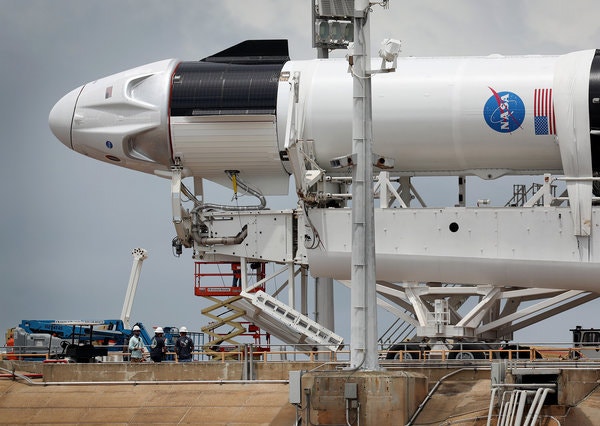
The SpaceX Falcon Rockets
Overview of the Chinese Space Program
Current Japanese Space Program
The ISS serves as a microgravity and space environment research laboratory in which scientific
experiments are conducted in astrobiology, astronomy, meteorology, physics, and other fields.
The station is suited for testing the spacecraft systems and equipment required for possible future l
ong-duration missions to the Moon and Mars.
It is the largest artificial object in space and the largest satellite in low Earth orbit,
regularly visible to the naked eye from Earth's surface.
It maintains an orbit with an average altitude of 400 kilometres (250 mi) by means of reboost manoeuvres
using the engines of the Zvezda Service Module or visiting spacecraft. The ISS circles the Earth
in roughly 93 minutes, completing 15.5 orbits per day.
The station is divided into two sections: the Russian Orbital Segment (ROS), operated by Russia;
and the United States Orbital Segment (USOS), which is shared by many nations.
Roscosmos has endorsed the continued operation of ISS through 2024, but had previously proposed
using elements of the Russian segment to construct a new Russian space station called OPSEK.
The station is expected to operate until 2030.
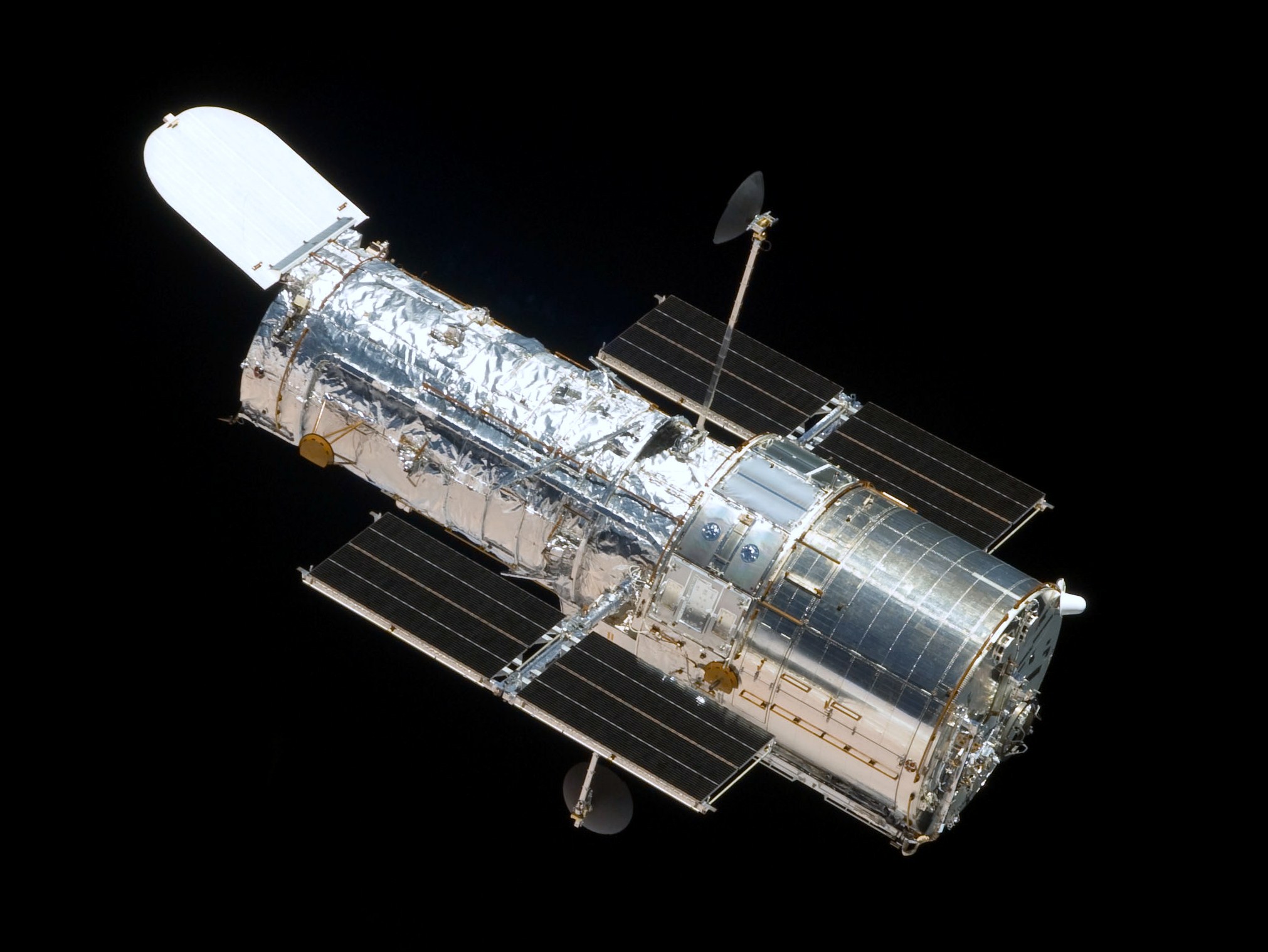

The Hubble Space Telescope is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990,
The Hubble telescope is named after astronomer Edwin Hubble.
Hubble features a 2.4-meter (7.9 ft) mirror, its four main instruments observe in the ultraviolet,
visible, and near infrared regions of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Hubble's orbit outside the distortion of Earth's atmosphere allows it to capture extremely
high-resolution images with substantially lower background light than ground-based telescopes.
It has recorded some of the most detailed visible light images, allowing a deep view into space.
Many Hubble observations have led to breakthroughs in astrophysics, such as determining the
rate of expansion of the universe.
Hubble is the only telescope designed to be maintained in space by astronauts.
Five Space Shuttle missions have repaired, upgraded,
and replaced systems on the telescope, including all five of the main instruments.
For more information on the designing of the Hubbble Telescope
Hubble Wikipedia
News images and videos can be seen here ,
Hubble Site


The Soyuz rocket is the workhorse for Russian manned space missions and has been used for that purpose
longer than any other vehicle. In the 1960s it began carrying cosmonauts into space and then to the Soviet Salyut and Mir stations.
Together with the US Space Shuttle, it ensured the transport of crews to and from the International Space Station.
To ensure that Soyuz will be able to carry out missions of this type from Europe’s Spaceport,
the launch infrastructure has been designed so that it can be easily adapted for manned spaceflight.
A Soyuz launcher took off from Europe’s Spaceport in French Guiana on 21 October 2011.
This was a historic event because it was the first time that a Soyuz was launched from a spaceport
other than Baikonur or Plesetsk. It also marked a breakthrough in the strategic cooperation between
Europe and Russia on launchers. The Soyuz launch vehicle that is used at Europe’s Spaceport is the Soyuz-2 version called Soyuz-ST.
Soyuz-2 has improved performance and is able to carry up to 3 tonnes into geostationary transfer orbit,
compared to the 1.7 tonnes that can be launched from Baikonur, in Kazakhstan.
For more information on the story of the Soyuz Rockets
Soyuz Wikipedia
Why not visit the UK`s Space Centre
Visit The Site
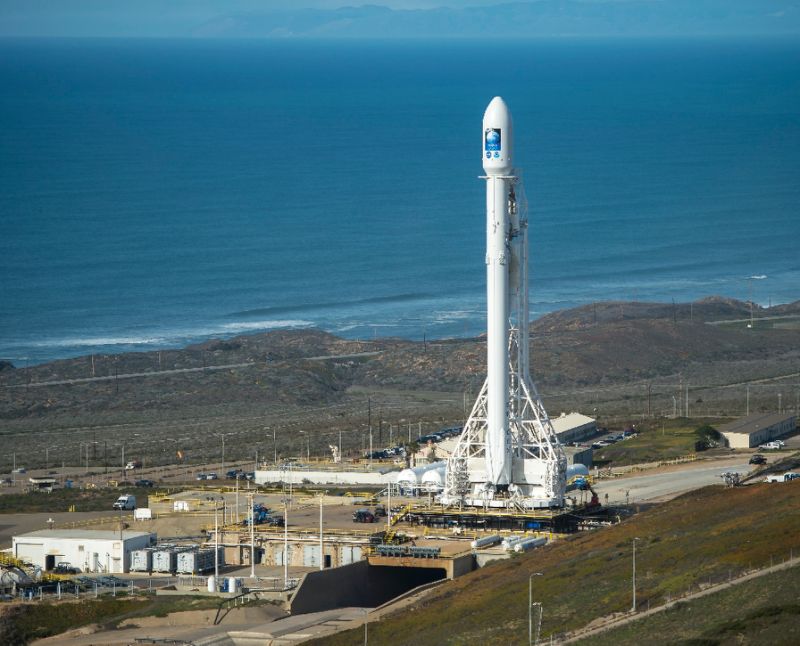


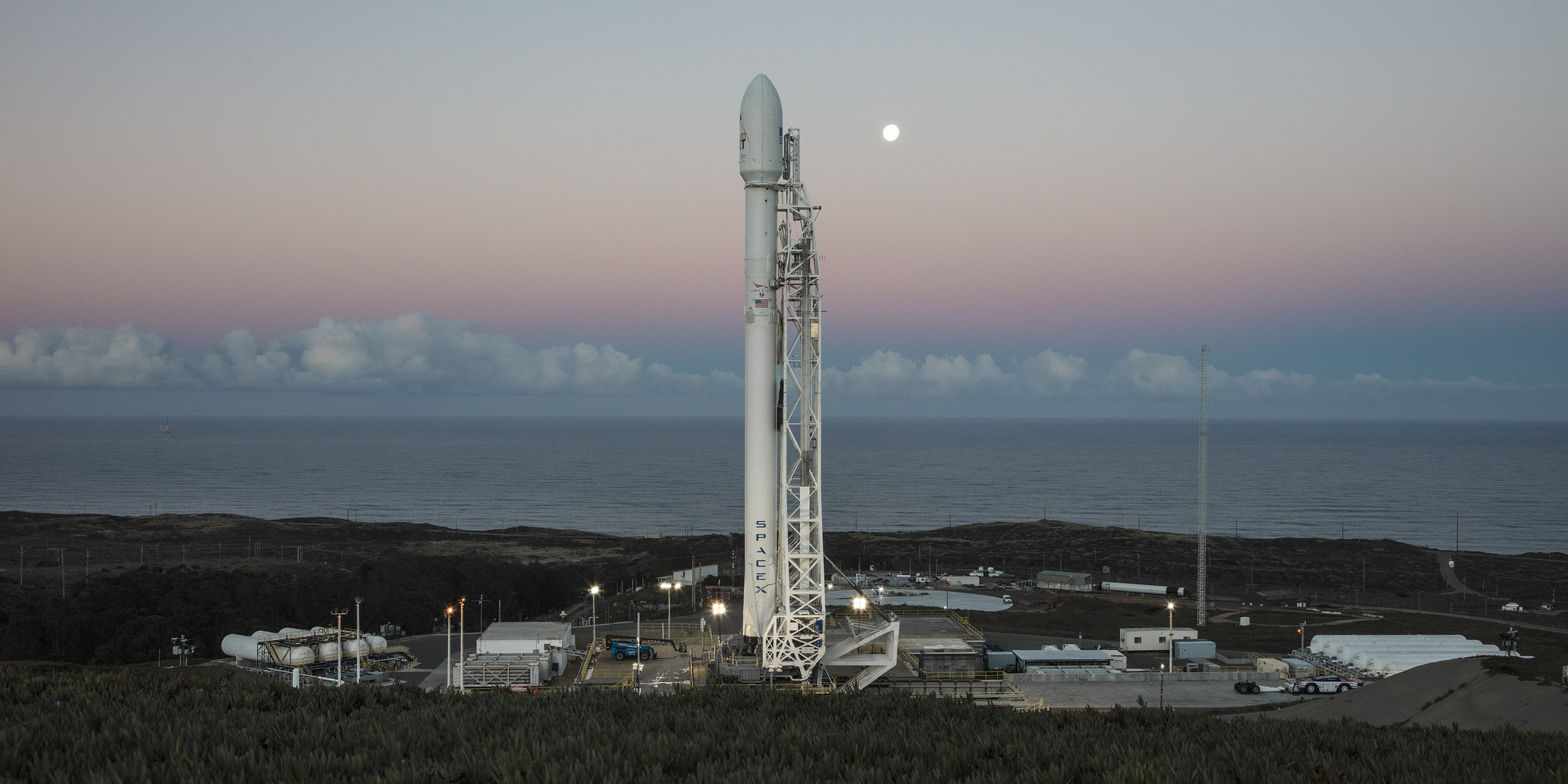
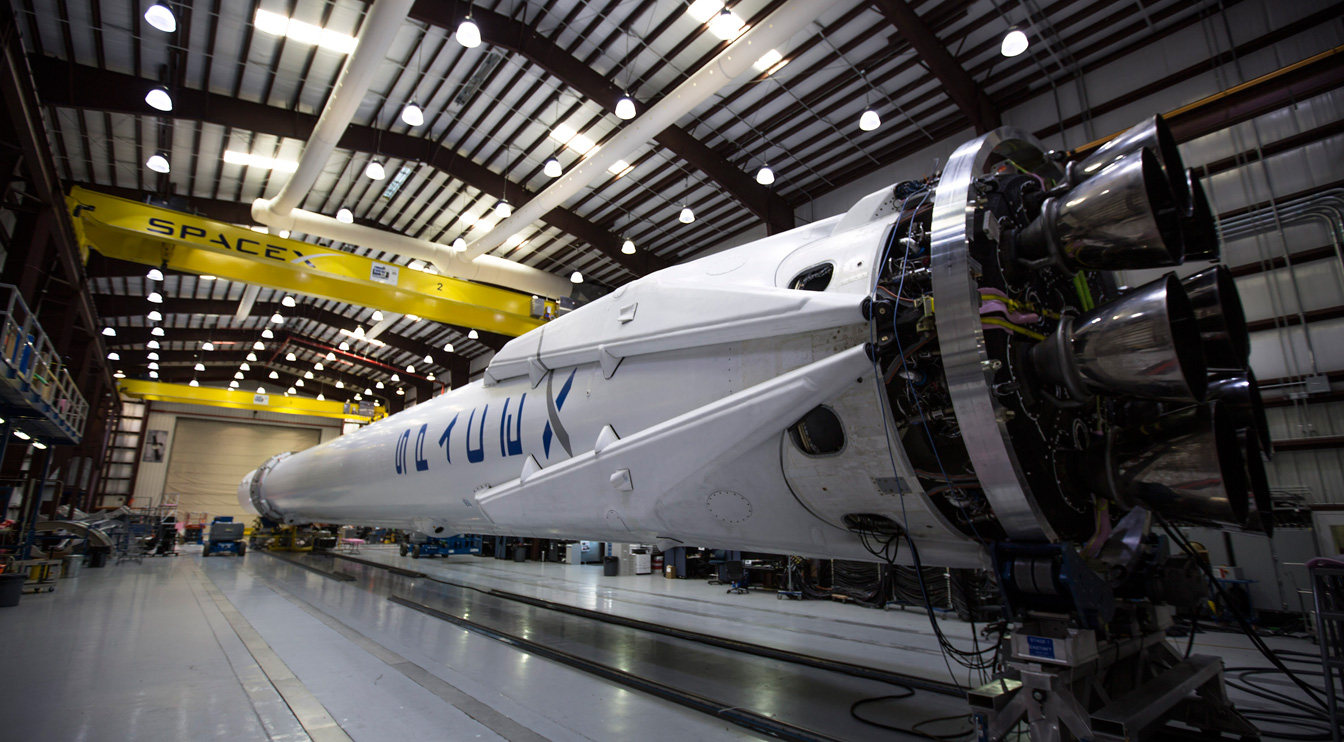
Falcon 9 is a reusable, two-stage rocket designed and manufactured by SpaceX for the reliable and safe
transport of people and payloads into Earth orbit and beyond. Falcon 9 is the world’s first orbital class
reusable rocket. Reusability allows SpaceX to refly the most expensive parts of the rocket,
which in turn drives down the cost of space access.
SpaceX offers competitive pricing for its Falcon9 and Falcon Heavy
launch services. Modest discounts are available, for contractually
committed, multi-launch Purchases. SpaceX can also offer crew
transportation services to commercial customers seeking to
transport astronauts to alternate lower Earth orbit destinations.
Aproxmittly $62M for Falcon and $90M Falcon Heavy if you have
any spare coins in your back pocket. With loads from 5.5mT to 8mT
respectively.
For more information on the story of the SpaceX Rockets
SpaceX Wikipedia
Visit the home of SpaceX
Visit The Site
The space program of the People's Republic of China is directed by the
China National Space Administration (CNSA). Its technological roots can be
traced back to the late 1950s, when China began a ballistic missile program
in response to perceived American (and, later, Soviet) threats. However,
the first Chinese crewed space program only began several decades later,
when an accelerated program of technological development culminated
in Yang Liwei's successful 2003 flight aboard Shenzhou 5.
This achievement made China the third country to independently send humans into space.
Plans currently include a permanent Chinese space station in 2022
and crewed expeditions to the Moon.
The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) was formed in 2003 after the merger of three
government space organizations into one. JAXA is responsible for all civilian space activities in Japan,
with activities ranging from basic space research to ongoing space missions.
Japan's human exploration program long predates the beginning of JAXA, i
ncluding numerous contributions to the International Space Station.
Its work on station includes the Kibo research module (including a robotic arm)
and regular cargo flights to ISS using the H-II Transfer Vehicle (HTV).
The country is also noted for several robotic exploration missions – Hayabusa's sample
mission from asteroid 25143 Itokawa and the lunar mission SELENE are examples –
and its new self-checking rocket, Epsilon.

I was born before any country had ever launched an object into space,
But only 6 of those countries have a truly substantial space program, capable of
launching and recovering people and or satellites into and from space and operate spacecraft.
We have come a long way in 60 years , where will we be in another 100 years.

Free JavaScripts provided
by
The JavaScript Source